半導体製造装置の交流磁場障害対策
- カテゴリ
-

-
- 対策機器・設備別
-
- 空調/衛生設備
- 電気設備
- 産業機械
- 建物/構造物
- 精密装置
- 嫌振装置
- 試験設備
-
- 障害別
-
- 振動
- 騒音
- 磁場
- その他
-
- 環境別
-
- 生活環境
- 交通
- オフィスビル
- 一般施設
- 工場
- 研究施設
-
- 建物・業界別
-
- ホテル/宿泊施設
- 病院/福祉施設
- オフィス/会議室
- 店舗/商業ビル
- 大学研究室/学校
- マンション/住宅
- プラント/工場
- 社会インフラ
-
- アクティブ磁場キャンセラによりSEM計測画像精度を改善
- 半導体製造ラインで使用されるSEM応用装置の観察画像にノイズが混入し、計測精度に問題を生じていた。これより、装置内部へ磁場キャンセラコイルを設置し、装置内外より発生する交流(AC)磁場への対策を行った。結果、装置レイアウトの変更なく画像ノイズを低減し、計測精度を改善することができた。なお本事例のケースでは、環境磁場レベルとしては元々装置許容値を満たしていたが、現地での装置セッティング等の内部要因にも起因するものか、障害を発生している状況であった。
SEMへの磁場影響
走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM:Scanning Electron Microscope)は電子線を絞って電子ビームとして対象物に照射し、その際に放出される2次電子を検出することで像を観察する。主に高真空中に対象物を置き、電子線で試料を走査することで、各座標の像を構築し表示する。電子ビームを使用するため、高分解能が必要とされる装置では磁場影響を受けやすい。
本事例は、装置内外より発生する交流磁場影響により、SEM画像に定常的なノイズが混入し、計測障害を生じていたケースである。装置及び磁場キャンセラコイル概略図を【図1】に示す。
-
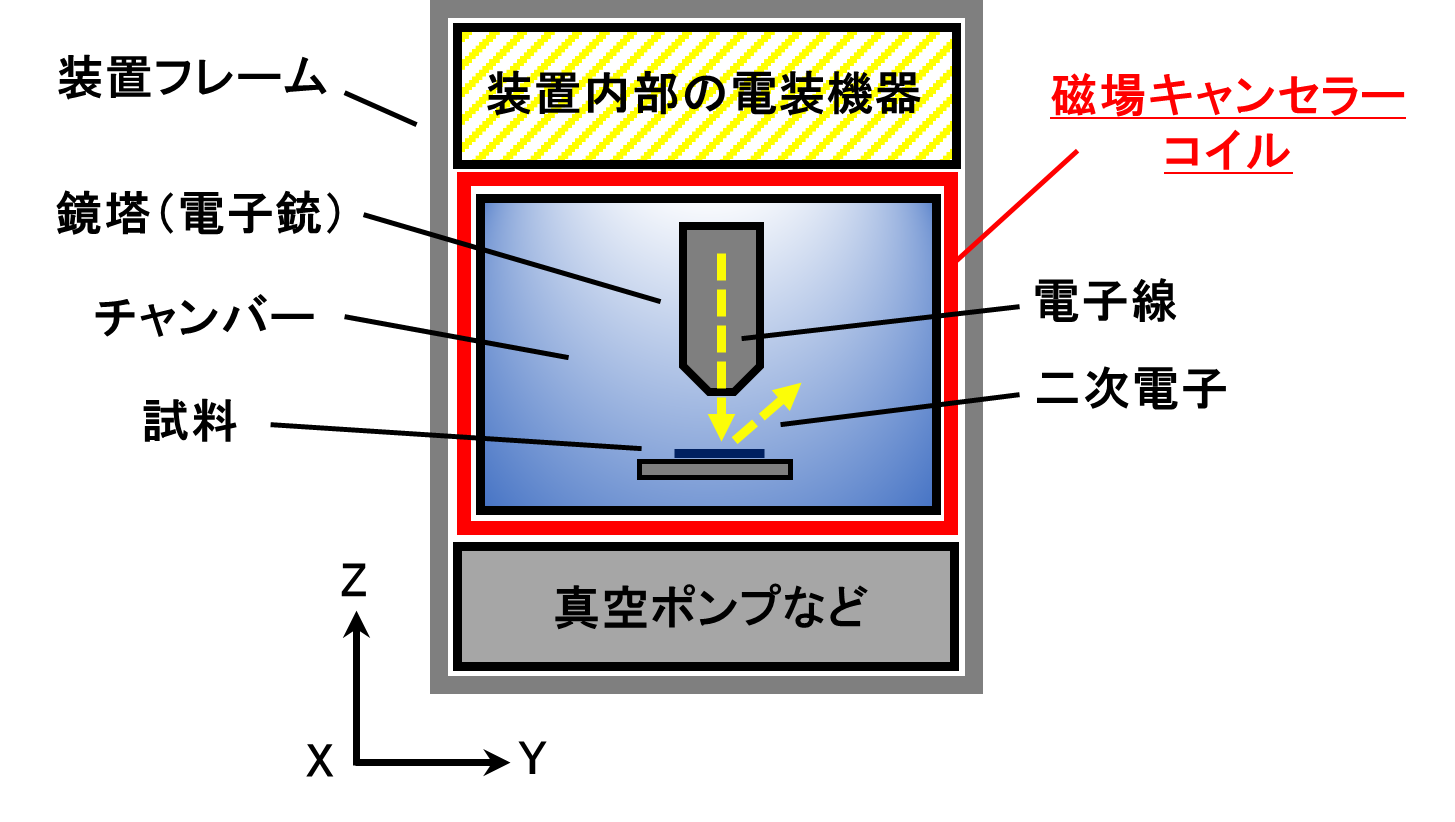
図1: 装置及び磁場キャンセラコイル概略図(側面)
磁場キャンセラによる対策結果
装置内部にコイルを設置し(【図1】概略図参照)、交流磁場対策を行った。対策前後のSEM観察画像を【図2】に、測定結果を【表1】、スペクトルデータを【図3】に示す。
本事例では、装置内部(フレーム内部)に設けられた電源系や装置周辺に設置された設備機器等から発生する磁場によって計測画像に縞状のノイズが混入していた。
【表1】に示すように、元々の周辺磁場環境としては許容値を満足していたが、装置運用開始後、計測画像にはノイズが混入する形となっていたため、実際の磁場感度は当初設定値よりも高い(許容レベルがより厳しい)のではないかということが原因として考えられた。
これに対しアクティブ磁場キャンセラ対策を行った結果、1/100以下に磁場レベルを低減し、【図2】のように計測画像精度を改善することができた。
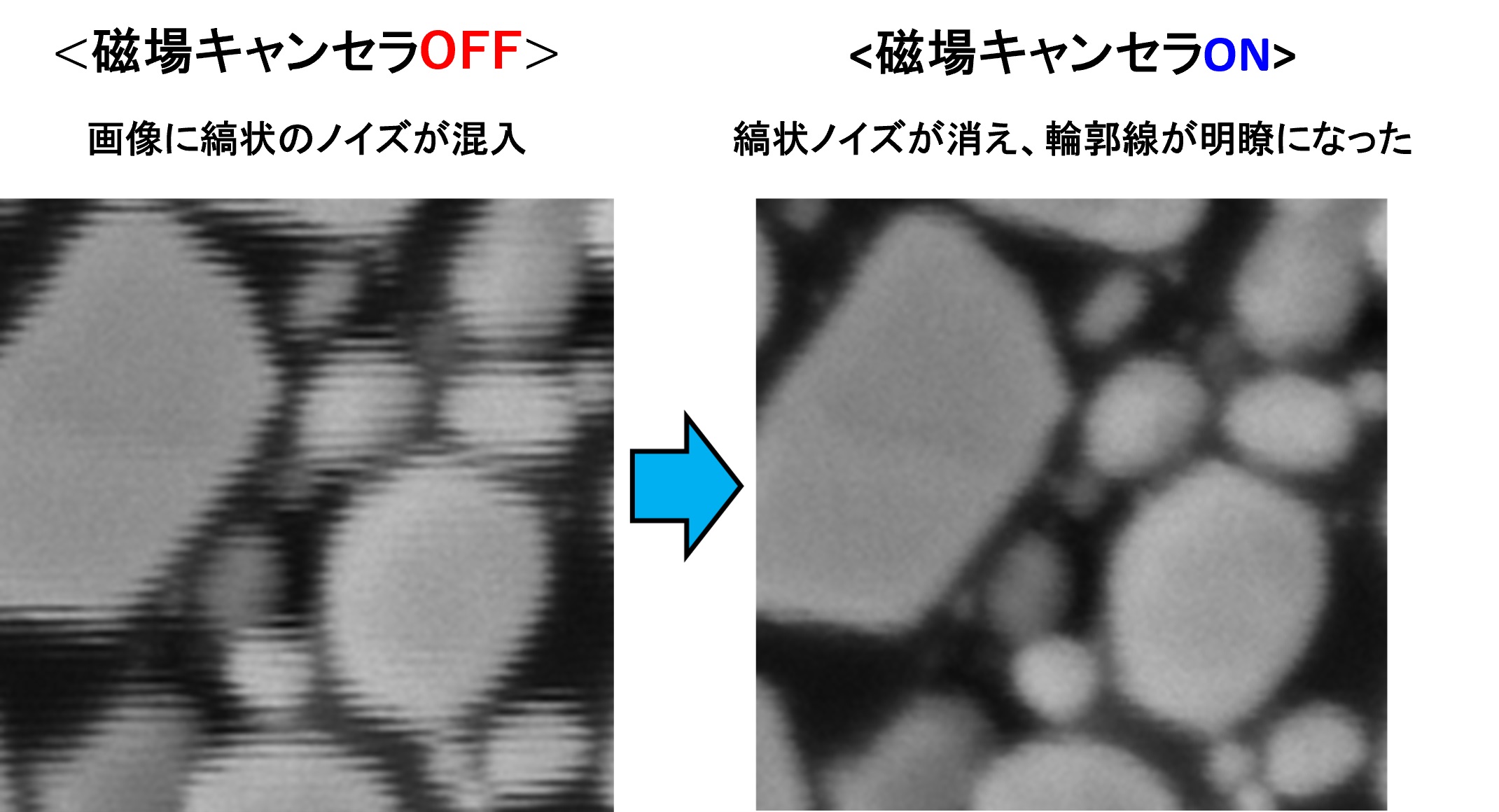
図2: SEM観察画像 (磁場キャンセラ対策前後)
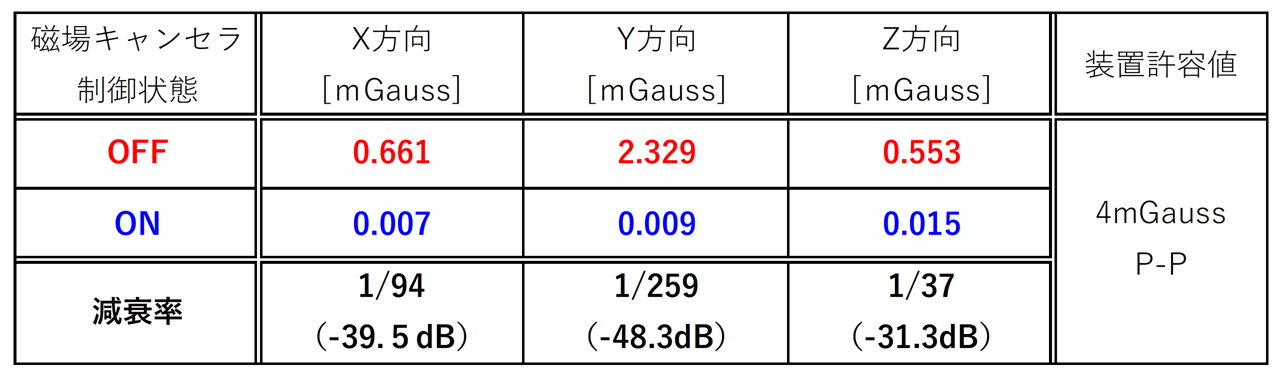
表1: 磁場キャンセラ効果(スペクトル最大成分、図3グラフ参照)
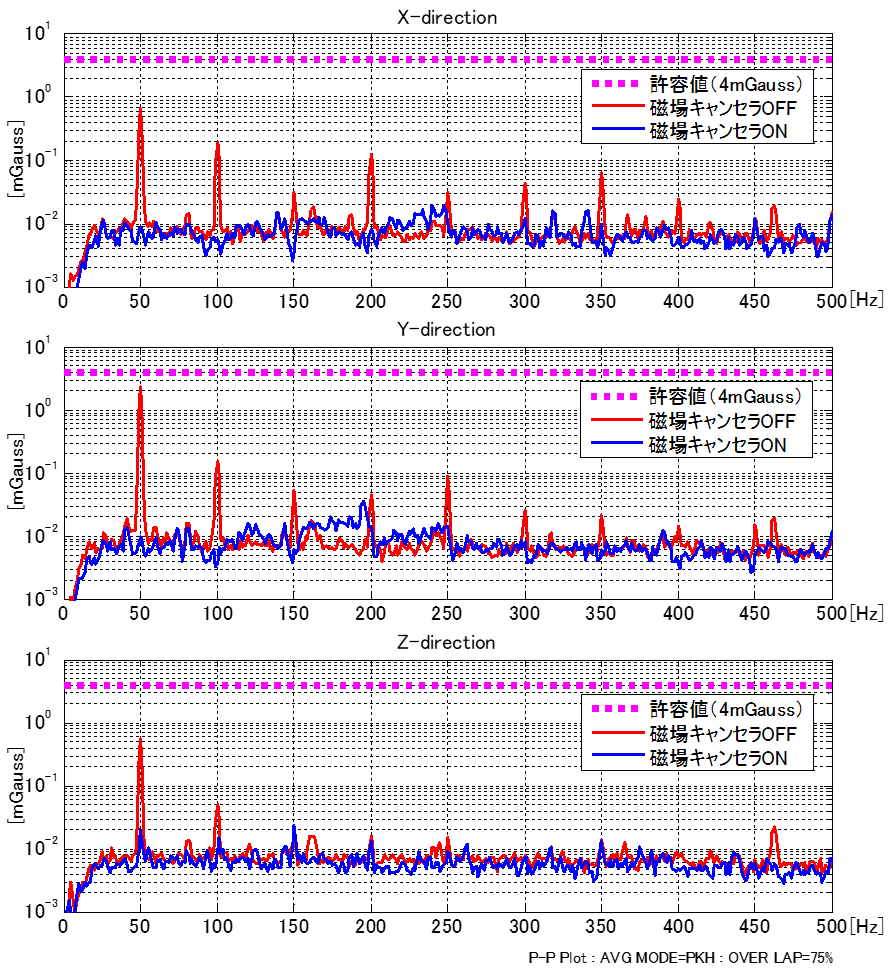
図3: 交流磁場スペクトル (磁場キャンセラ対策前後)