Countermeasure by Active Vibration Isolation for the precision equipment with moving stage
- Category
-

-
- Type of equipment/device
-
- Air conditioning/Sanitary equipment
- Electrical equipment
- Buildings/Structures
- Precision equipment
- Vibration-sensitive equipment
-
- Vibration obstacle phenomena
-
- Vibration
- Noise
- Magnetic fields
-
- Type of usage environment
-
- Living environments
- Office buildings
- General facilities
- Factories
- Research facilities
-
- Building type
-
- Hotels/Accommodations
- Hospitals/Welfare facilities
- Office/Meeting rooms
- Store/Commercial buildings
- University Labs/Schools
- Condominiums/Houses
- Plants/Factories
-
- Countermeasure by Active Vibration Isolation for the precision equipment with moving stage
- Fine process equipment (including inspection and analysis) represented by semiconductor manufacturing requires very quiet vibration environment. However, the equipment body itself generates the vibration from the moving component (XY stage, gantry, etc.) during operation. And such vibration is increasing in accordance with semiconductor wafers and liquid crystal panels size enhancement. We use stage feedforward control technique to suppress the vibration caused by the driving force of moving component.

Stage Feed Forward control (SFF control)
The vibration sensitive equipment is mounted on the Active Vibration Isolation system in the normal micro-vibration countermeasures, and the vibration transmitted from the installation floor is detected by the acceleration sensors for the active isolation control.
Some equipment mounted on the Active Vibration Isolation system have built-in stage, and there are some cases that the vibration generated by the moving stage in order to improve productivity causes the problem.
When both vibration isolation and vibration control performance are required in this way, it is necessary to determine the excitation force when the stage is being driven.
The excitation force of the stage is estimated by installing the accelerometer on the stage or receiving the stage driving signal (corresponding to acceleration) from the driver, and used as the feedforward input to achieve both vibration isolation and control performance.
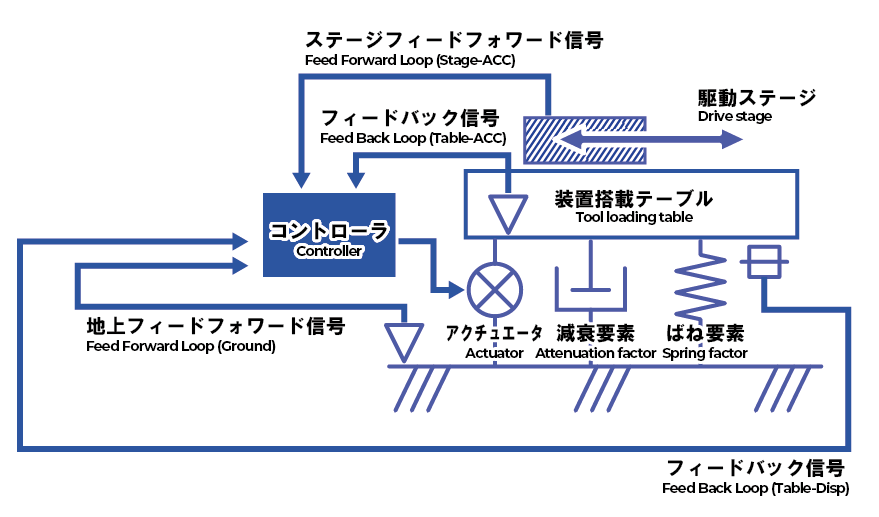
Figure1: Active Vibration Isolation model using stage feedforward control
Measurement results of control performance while high-speed stage driving
Figure 2, 3 and Table 1 show the comparison of the control effect based on the output of the built-in sensor of the Active Vibration Isolation system. By the introduction of SFF, both displacement and acceleration during stage operation have been improved. The displacement becomes approximately 1/10 and the acceleration approximately 3/4 for the X direction stage driving.
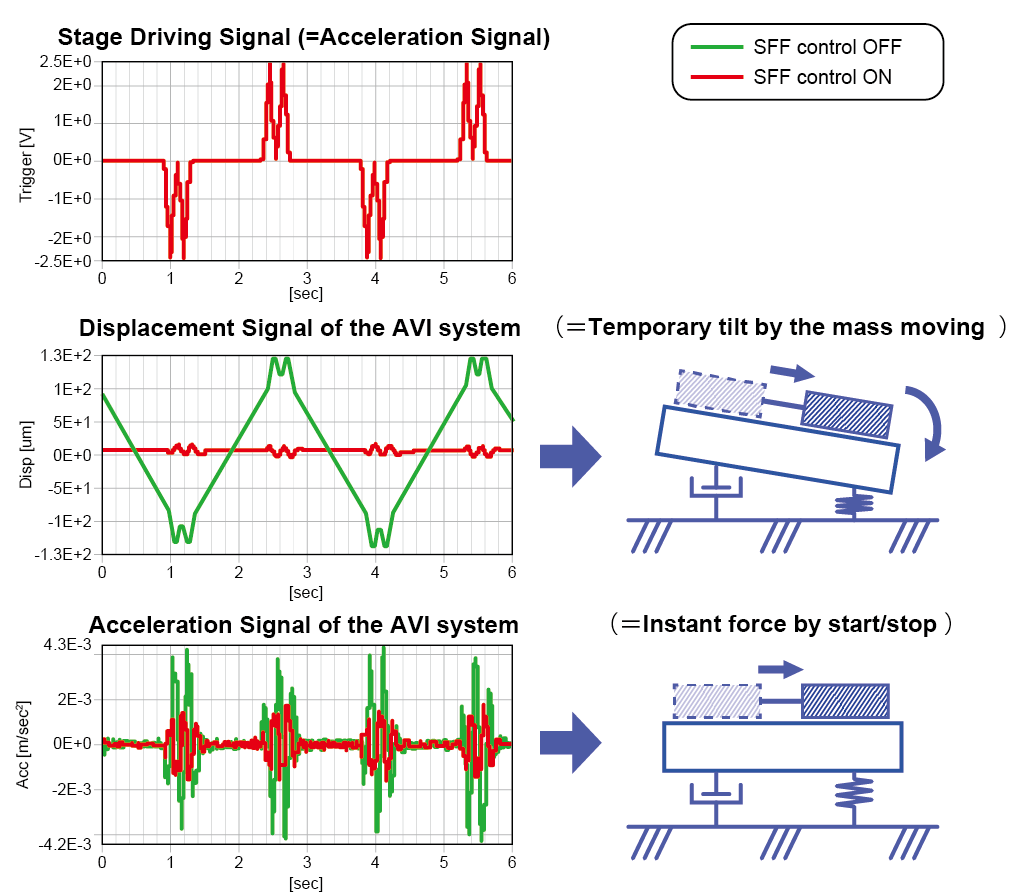
Figure 2: SFF evaluation data ①
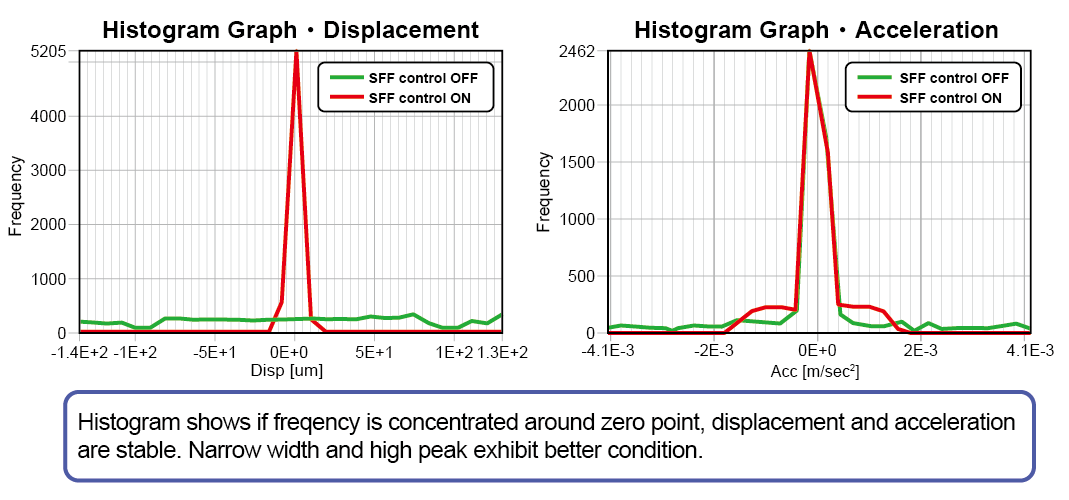
Figure 3: SFF evaluation data ②
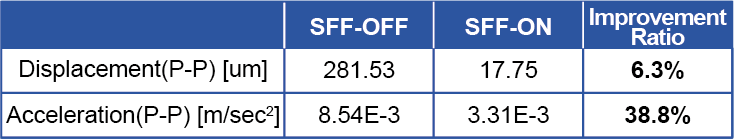
Table 1: SFF Evaluation data
Actual measurement results (vibration comparison in tripartite graph)
FIG. 4 shows floor vibration data (red line) and Active Vibration Isolation system data (blue line / on the floating table). It exhibits excellent vibration isolation performance, especially in the 1 to 10 Hz band, with nearly minus 20 dB (1/10) in each direction.
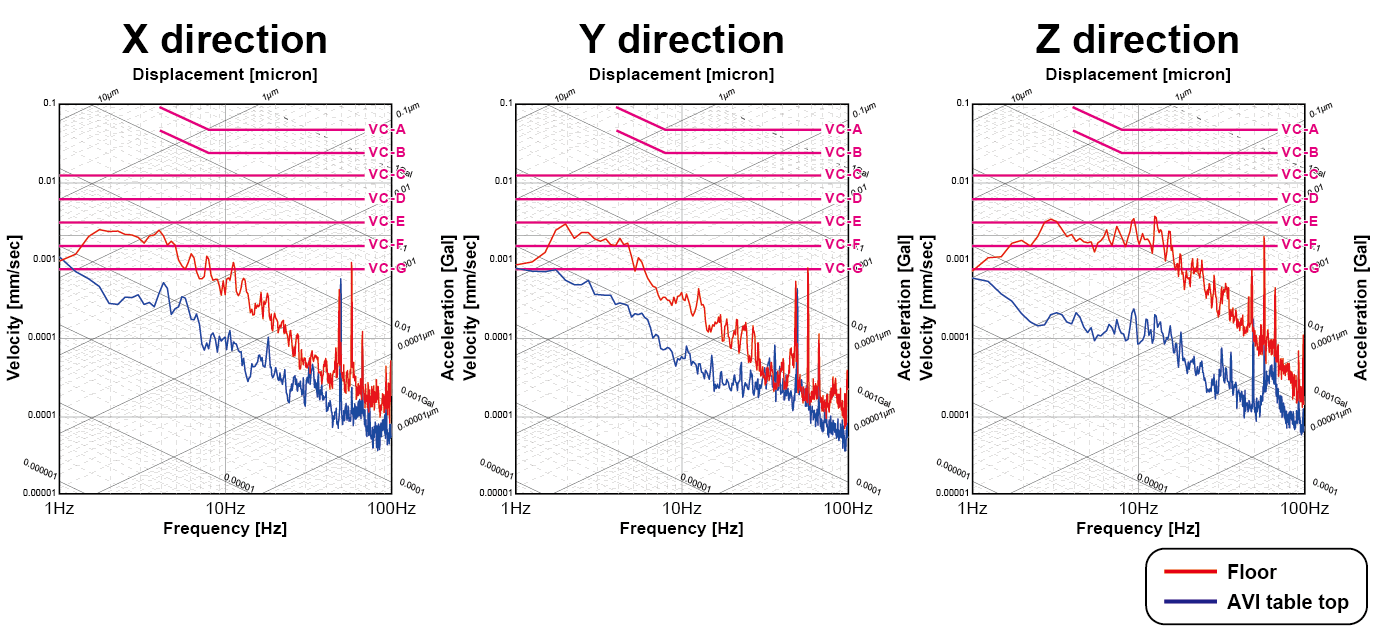
Figure 4: Vibration Isolation Performance: Vibration Spectrum
Averaging: Peak Hold (0-P)